Do you view vegetable oils as a positive in your healthy lifestyle? There is a fairly large percentage of the population that perceives vegetable oils as healthy, and even many of our mainstream nutrition organizations recommend that we eat them, because “according to them” unsaturated fats are a much healthier option over saturated fats.
However, an abundance of studies have now demonstrated that these oils can cause serious harm due to the fact that the fatty acid composition is severally altered and unlike anything our body has been exposed to throughout evolution. (1)
This is leading to some major physiological changes within our bodies and contributing to a host of chronic and metabolic health issues.
In this article, the vegetable oils I’m referring to are industrialized seed oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, etc… because, even though these oils aren’t necessarily made from vegetables, their oils are commonly referred to as “vegetable oils.”
You see, vegetable oils are oils that have been extracted from various seeds. The most common include rapeseed (canola oil), soybean, corn, sunflower, safflower and grapeseed oil. Unlike coconut oil or olive oil that can be extracted by pressing, these new-fangled oils have to be extracted in very unnatural ways.
Olive oil and coconut oil are extremely healthy fats, while vegetable oils – which are relatively new to our system – contain very large amounts of the biologically active polyunsaturated fat commonly known as Omega 6 fatty acids. And although Omega 6 fats are essential to the body, in excess they become toxic and very harmful due to their highly pro-inflammatory response in the body.
Let’s take a look at 5 reasons why vegetable oils can be downright harmful
1.Vegetable Oils Contribute to Inflammation
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are used to make substances called eicosanoids in the body which are modified fatty acids that sit in our cell membranes. These modified fatty acids then play a critical role in bodily functions like cellular messaging, immunity and inflammation. (2)
In general, eicosanoids made from Omega-6s are pro-inflammatory, while those made from Omega-3s are anti-inflammatory. (3)
I am sure that many of us can relate to having pain from an injury, a headache or a strain of some sort and turned to aspirin or ibuprofen to relieve it. Essentially what these drugs are doing is inhibiting the eicosanoid pathways to reduce inflammation.
Now, whereas acute inflammation is good and necessary in order to help heal your body from trauma or damage (such as when you twisted your ankle or hit your head), having systemic inflammation all over your body is very bad.
These different fatty acids compete with each other: the more Omega-6 you have, the more Omega-3 you need and the less Omega-6 you have, the less Omega-3 you need. (4)
Having high Omega-6 and low Omega-3 is a recipe for disaster, but this is the case for people eating a Western diet. Put simply, a diet that is high in Omega-6 but low in Omega-3 contributes to inflammation. A diet that has balanced amounts of both Omega-6 and Omega-3 reduces inflammation. (5)
It is now believed that increased inflammation contributes to various serious diseases, including cardiovascular disease, arthritis, depression and even cancer.
Bottom Line: Eicosanoids, signaling molecules made from Omega-6 and Omega-3 fats, are crucial in regulating inflammation in the body. The more Omega-6s you take in through your diet the more systemic inflammation you will have.
2. Vegetable Oils Change the Fatty Acid Composition of The Body’s Cells
There are two types of fatty acids that are termed “essential” – because the body can’t produce them. These are the Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids. It is absolutely essential for the human body to get these fatty acids from the diet, but it must get them in a certain balance.
While humans were evolving, our Omega-6: to Omega-3 ratio was between 1:1 and 4:1. However, today, our ratio is 16:1 or higher, of course varying between individuals. (6)
These fatty acids aren’t just inert structural molecules or fuel for the cell’s mitochondria, they serve vital functions related to processes known to affect various systems like the immune system. (7)
When the balance of Omega-6s and Omega-3s in the cell is off, things can start to go terribly wrong.
Another problem is the relative unsaturation of these fatty acids. Polyunsaturated fats have two or more double bounds, while monounsaturated fats have one and saturated fats have no double bonds. The more double bonds in a fatty acid, the more reactive it is. Polyunsaturated fats are prone to react with oxygen, which can cause chain response, damaging other structures and perhaps even vital structures like DNA. (8, 9)
These fatty acids tend to sit in the cell membranes, increasing harmful oxidative chain reactions.
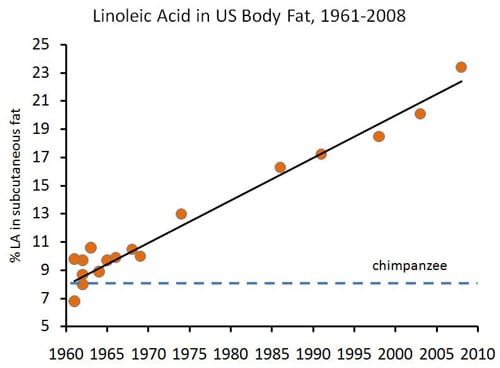
According to this graph, our body fat stores of Linoleic acid (the most common Omega-6 fat) have increased 3-fold in the past 50 years.
That’s right, excessive consumption of vegetable oils leads to actual structural changes within our fat stores and our cell membranes.
I don’t know about you, but I find that to be a pretty scary thought.
Bottom Line: Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids are biologically active and humans need to eat them in a certain balance to function optimally. Excess Omega-6s in our cell membranes are prone to harmful chain reactions.
3. Vegetable Oils Are Loaded With Trans Fats
Trans-fats are unsaturated fats that are modified to be solid at room temperature. These fats are highly toxic and are associated with an increased risk of various diseases, like heart disease, cancer, diabetes and obesity. (10, 11, 12)
They are so bad that even the governments around the world have started taking action, setting laws that command food manufacturers to reduce the trans-fat content of their foods.
However, a little known fact is that vegetable oils often contain massive amounts of trans-fats .In one study that looked at soybean and canola oils found on store shelves in the U.S., about 0.56 percent to 4.2 percent of the fatty acids in them were toxic trans-fats. (13)
If you want to reduce your exposure to trans-fats (as you should) then it’s not enough to avoid common trans-fat sources like cookies and processed baked goods, you also need to avoid vegetable oils.
Bottom Line: Trans-fats are highly toxic and associated with multiple diseases. Soybean and canola oils commonly sold in the U.S. contain very large amounts of trans-fats.
4. Vegetable Oils Raise Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death in the world. (14)
Whereas saturated fats were once considered to be key players, newer studies prove that they are harmless. (15, 16)
Now the attention is increasingly being turned to vegetable oils.
Multiple randomized controlled trials have examined the dramatic effects that vegetable oils can have on cardiovascular disease. (17, 18, 19)
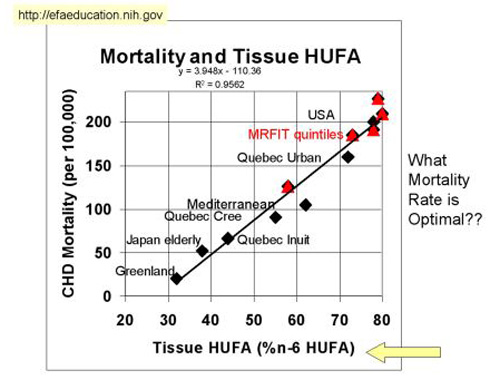
This chart shows the USA right at the top with the greatest risk of death from cardiovascular disease and the highest consumption of Omega-6’s. Even though this study only shows a correlation, it makes perfect sense given that inflammation is a known contributor to these diseases.
I’d like to point out that there are some studies showing that polyunsaturated fats reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, but the problem is that they don’t make the distinction between Omega-3s and Omega-6s, which is absolutely crucial.
When this distinction is taken into account, they find that Omega-6s actually increase the risk, while Omega-3s have a protective effect. (20)
Bottom Line: There is evidence from both randomized controlled trials and observational studies that vegetable oils can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
5. Vegetable Oil Consumption is Associated with Various Other Diseases
Because polyunsaturated fats are so tightly involved in the function of the body on a molecular level, it makes sense that they could affect other diseases as well.
Many of these associations aren’t well studied in humans yet, but there are both observational studies and animal studies linking vegetable oils to other serious diseases:
- In one study, increased Omega-6 in breast milk was associated with asthma and eczema in young children. (21)
- Studies in both animals and humans have linked increased Omega-6 intake to cancer. (22)
- One study shows a very strong correlation between vegetable oil consumption and homicide rates. (23)
- The Omega-6: to Omega-3 ratio in blood has been found to be strongly associated with the risk of severe depression. (24)
This is just the tip of the iceberg. Inflammation, and therefore vegetable oil consumption, is associated with a wide range of serious diseases and it is beyond the scope of this article to cover all of them.
I am personally convinced that vegetable oils, along with added sugar and refined flour are the key players in the obesity and chronic disease epidemics our Western culture is battling with today.
Take Home Message:
If you want to be healthy, feel good and lower your risk of serious diseases, then you should consider avoiding vegetable oils. For a complete list of my preferred oils, see “Tony’s Top Picks for Cooking and Eating” on page 201 of my latest book entitled: